Drug test kits have revolutionized the way we approach substance detection, offering quick and accessible solutions for identifying the presence of drugs in various samples. Behind the simplicity of these kits lies a fascinating blend of chemistry, immunology, and molecular biology.
In this article, we delve into the science that powers drug test kits, exploring the mechanisms that enable them to accurately detect a wide range of substances.
1. Immunoassay Tests: Antibody-Antigen Interaction
Table of Contents
The cornerstone of many drug test kits is the principle of immunoassay. Immunoassay tests utilize the specific interaction between antibodies and antigens. In the context of drug testing, antigens are drug metabolites or substances of interest, while antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system in response to these substances.
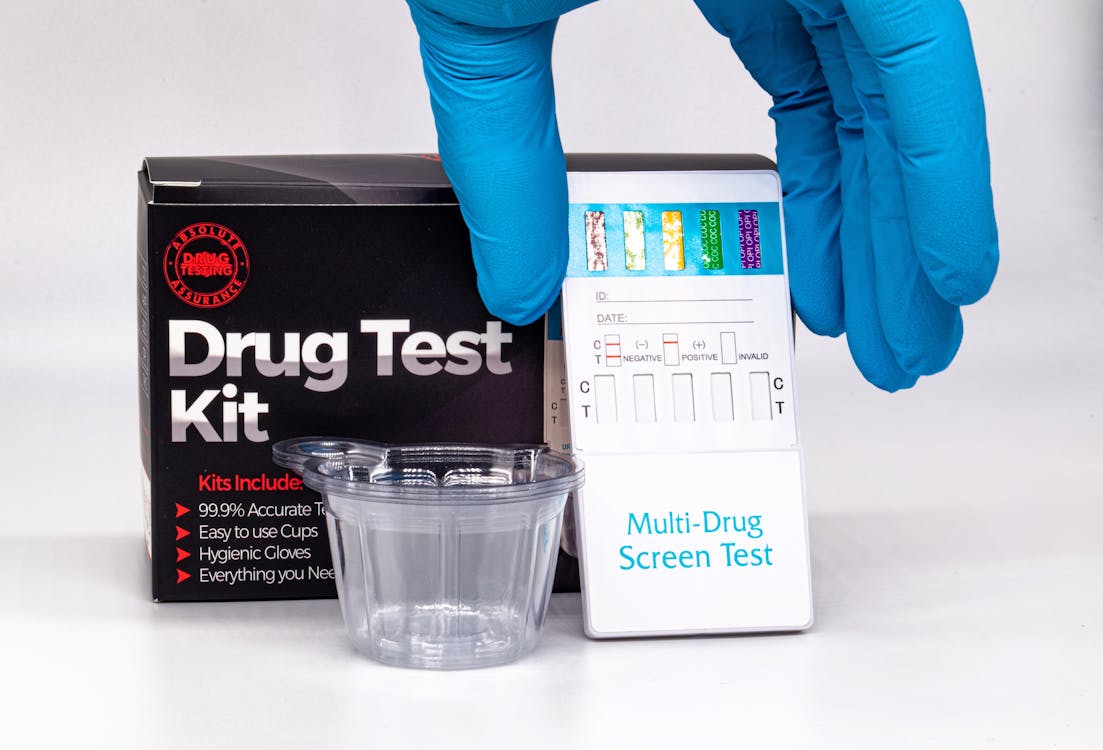
2. Urine Tests: Unveiling Drug Metabolites
Urine drug tests, one of the most common types of drug test kits, rely on immunoassay techniques to detect drug metabolites in urine samples. When a person ingests a drug, their body metabolizes it into various byproducts, which are then excreted through urine. Drug test kits contain antibodies that are specifically designed to recognize and bind to these drug metabolites.
When a urine sample is introduced to the test kit, any drug metabolites present in the sample will bind to the antibodies. This binding triggers a reaction that produces a visible result, often in the form of color changes or the appearance of lines on the testing strip. The intensity of the reaction is proportional to the concentration of the drug metabolite in the sample.
3. Saliva Tests: Rapid Detection of Recent Use
Saliva drug test kits are designed to detect recent drug use by analyzing traces of drugs in saliva. These tests are particularly useful for situations that require immediate results, such as workplace testing or roadside checks.
Similar to urine tests, saliva tests employ immunoassay techniques. A swab soaked in the individual’s saliva is placed in the test kit. If any drug residues are present in the saliva, they will react with the antibodies in the kit, producing a visible signal that indicates the presence of drugs.
4. Hair Tests: A Chronicle of Drug Use
Hair drug test kits take a different approach by focusing on the detection of drug metabolites that are incorporated into the hair shaft over time. When a person uses drugs, the metabolites enter their bloodstream, and a fraction of these metabolites are deposited in the hair follicles as hair grows. This fact is the reason why hair tests can cover such a long period of past drug use.
In hair tests, small samples of hair are collected and prepared for testing. The hair is typically washed to remove external contaminants, and then the internal components of the hair shaft are analyzed. This process allows for the identification of a historical pattern of drug use, as different segments of the hair correspond to different time periods.
5. Surface Tests: Uncovering Residues
Surface drug test kits serve a unique purpose by detecting drug residues on various surfaces. Law enforcement agencies and security personnel use these kits to identify drug traces on objects, clothing, or other items.
These kits work by using specially treated swabs to collect samples from the surface being tested. If any drug residues are present, they will interact with the swab’s reagents, leading to a color change or other visible indication of drug presence.
Conclusion
Drug test kits are a testament to the ingenuity of science and technology. By harnessing the principles of immunoassay and other biochemical reactions, these kits offer a reliable and accessible way to detect the presence of drugs in various samples.
From urine and saliva tests to hair and surface tests, the science behind drug test kits enables individuals, professionals, and organizations to make informed decisions about drug use and safety.
- How To Create A Safe And Comfortable Home Environment For In-Home Care In Boca Raton? - July 16, 2024
- 10 Trendy Black Nail Ideas To Elevate Your Nail Game - May 6, 2024
- Getting A Free Divorce In Virginia? Here’s What To Expect - April 24, 2024





No Comments