Cisco networking is a vast subject to study. MPLS or Multiprotocol Label Switching is a subject to study under the umbrella of Cisco networking for taking network-related exams like CCNA and others. However, you will read the brief about MPLS in this blog. This will give you a heads-up before preparing this subject at full speed.
A brief definition of MPLS:
Table of Contents
MPLS is a data forwarding technique. Network speed and control flow get a boost using the latest MPLS or Multiprotocol Label Switching technique.
While working with MPLS, the data has the advantage of flowing directly in a path via labels. There is no complexity or requirement of looking up at routing tables at every halt or stop.
How does this MPLS work exactly?
LSPs or Label Switched Paths are paths amongst the router pair used across the set of MPLS networks.
- First, a packet gets assigned to FEC or Forwarding Equivalence Class as it enters the network. FECs help identify the class of packets for their similarities or differences in data type or intended direction.
- Based on this information, packets get a label by the ingress node. This further gets encapsulated in LSP.
- The labeled packet then moves through transit nodes. These nodes usefully direct the data in the packets through the passage as instructed in the packets initially. These stops at nodes are not based on IP lookups.
- At the final stop of the engress node, the label is removed from packets. Data is then moved ahead through IP routing.
Basic information on the label stack inside an MPLS:
A label stack has at least four layers or parts:
Label value: It has ample information for routers in the data passage to direct the packet further.
Traffic class field: Makes the differentiation between Explicit Congestion Notification and existing Quality of Service.
Bottom of stack flag: It shows the last label in the average/regular label stack.
TTL field: Decides the hops a data should go through the passage before discarding the same.
Is MPLS defined under Layer 2 or Layer 3?
Cisco networking admins and aspirants face confusion regularly regarding the MPLS setup and category of Layer 2 or Layer 3. Note that MPLS doesn’t quite fit into the original OSI-seven-layer hierarchy. Instead, it’s fine to call it the Layer 2.5 technique.
This layer separates MPLS from the regular message or data forwarding technique. We already understood from above that MPLS is the best for creating forward tables for any existing protocol.
A clear difference and understanding between SD-WAN and MPLS:
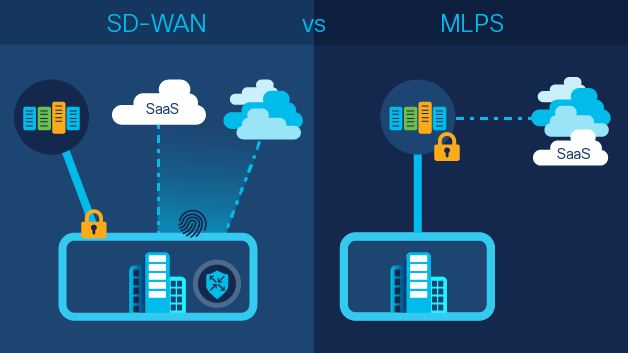
Network professionals consider SD-WAN and MPLS as similar. They think or work around them both as a “This or That” situation. However, reality shows that both these techniques have a particular use in the modern WAN system.
There’s scope for SD-WAN to eradicate MPLS in the later years. Though, that’s at least a decade or so away. Right now, companies are learning and starting to depend on hybrid networking systems. It includes cloud storage, cloud computing, and similar applications.
SD-WAN is SDN’s application conceptualizing under WAN. In other words, the SD-WAN application ensures the best path for sending the required traffic across.
SD-WAN can transport any traffic, being transport-agnostic overlay, including MPLS. Using SD-WAN is advantageous to centralize the traffic’s path across all WAN devices.
However, via MPLS, traffic paths are already determined in the data packet. Changing the path can be quite the task here when the data is already in transit. The changes aren’t point-and-click here in full honesty.
The data delivering performance has a guarantee when using MPLS. However, there is a data performance guarantee in SD-WAN. It’s rather best in choosing an efficient path but gives no assurance of the best delivery.
Verdict between SD-WAN and MPLS concludes to the latter for time-sensitive and public data transfer needs. You mustn’t load MPLS labeled data packets which the public server can’t handle or transmit efficiently.
Conclusion:
MPLS is the technique to forward data across a predetermined path using the nodes, fields, and labels attached to the data packets. Overall, it’s an interesting topic to study in the Cisco Network main exams.
You can even get ample information for MPLS by clicking here: https://cciedump.spoto.net/blog-888. Also, get the detailed intel on the updated dumps, test papers, and other study material there.
- How To Create A Safe And Comfortable Home Environment For In-Home Care In Boca Raton? - July 16, 2024
- 10 Trendy Black Nail Ideas To Elevate Your Nail Game - May 6, 2024
- Getting A Free Divorce In Virginia? Here’s What To Expect - April 24, 2024





No Comments