Gelatin is an edible material made from the collagen of animal body parts such as the bones, skin and connective tissue of cattle, pigs, chicken, and fish that is used in food as a gelling agent, in pharmaceuticals, and in cosmetics. Major feedstock for gelatin manufacturing is pigskin, accounting for 38 percent, bovine skin for 33 percent, bovine bone for 26 percent and fish and poultry for 3 percent. Most gelatin suppliers are operating at 90-95 percent capacity in order to meet the demands from the market. When dry, gelatin is brittle and when it is moistened it becomes gummy and is colorless and flavorless.
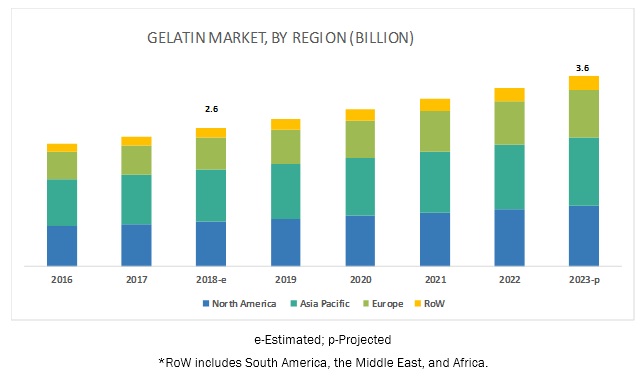
The global gelatin market size in terms of volume is expected to reach 420 KT (kiloton) by 2020, growing at a CAGR (compound annual growth rate) of 2.3 percent. The food industry is the single largest end-user industry for gelatin, accounting for 64 percent of the market, followed by pharmaceuticals for 34 percent. However, the demand from pharmaceuticals is growing at a higher CAGR of 4-5 percent while the demand from the food industry is growing at a CAGR of 2-3 percent. High market maturity regions are the U.S. and Europe, while medium maturity regions are India, China, Japan, and Brazil, and low market maturity regions are Africa and the Middle East.
Gelatin Health Benefits And Global Gelatin Market Growth
Although the first use of gelatin for food purposes can be traced back to the 1400s, the popularity of gelatin grew in the 1800-1900s due to its versatility and is now gaining further popularity due to the health benefits it provides. Gelatin is a great source of protein, amino acids, and collagen, consisting of 98-99 percent protein and amino acids such as Glycine, Proline, Valine, Hydroxyproline and Glutamic acid. As people across the world are becoming more health-conscious, there is a greater demand for natural products that can improve health and reduce the need for medicines. The varied health benefits of gelatin are therefore expected to significantly improve the global gelatin market growth.

Image Source: organika.com
- Improved Bone and Joint Health – Gelatin has been found to be helpful in improving bone and joint health overall and in treating bone problems such as osteoarthritis, by significantly reducing pain and stiffness in the joint. Gelatin supplements are also considered to be helpful for athletes in reducing joint pain as a result of exertion. The reported side effects have only been unpleasant taste and feelings of fullness. The amino acid Lysine found in gelatin also helps in strengthening bones by helping the body in absorbing calcium. Since Lysine is not produced by the human body and has to be incorporated through diet, gelatin is a convenient means of supplying the body with Lysine.
- Improved Skin and Hair – Apart from improving skin and hair by applying products externally taking specific supplements can help improve the skin and hair from within. Including gelatin products in the diet or taking gelatin supplements has been found to improve the skin moisture, density and elasticity significantly as well as improve hair growth, texture, and thickness. Gelatin is also effective in treating hair loss conditions such as alopecia.
- Weight Loss – Gelatin in the form of sugary chewy candies, baked goods and marshmallows may be fatty, however, consuming gelatin in a low sugar form has been shown to help in weight loss. As gelatin is fat-free and carbohydrate-free and has high protein, it is low in calories. In addition, gelatin helps people feel full longer because it leads to a rise in the hormones of the body that reduce appetite. Gelatin can be taken in the form of supplements, added to soups and broth, and to low-fat beverages.
- Diabetes Control – Diabetes has emerged as one of the most common lifestyle diseases around the world, with approximately 415 million people around the world suffering from it. People with diabetes tend to lose collagen even faster than those without diabetes. Low collagen levels can cause fatigue, muscle weakness, joint pain, skin rashes, and body aches. Gelatin acts as a great source of collagen and serves to counteract symptoms of low collagen. In addition, for those suffering from type 2 diabetes, gelatin helps in controlling blood sugar levels and reducing HbA1C readings.
Although there are numerous health benefits of gelatin that are driving the growth of the market, there are challenges that the market faces. Substandard quality of gelatin is a significant concern, and the growing vegan movement has also led to the development of vegan-alternatives for gelatin. However, the high costs involved in using materials such as sea-weed for gelatin has reduced their viability as an effective substitute.
The health benefits and lack of suitable alternatives are expected to drive the growth of the gelatin market in the coming years. Apart from the direct health benefits of gelatin, it is used to form the base of pharmaceutical syrups, capsules, and hard and soft gel tablets.
- How To Create A Safe And Comfortable Home Environment For In-Home Care In Boca Raton? - July 16, 2024
- 10 Trendy Black Nail Ideas To Elevate Your Nail Game - May 6, 2024
- Getting A Free Divorce In Virginia? Here’s What To Expect - April 24, 2024





Zachery
•5 years ago
Great article.